1. Introduction
- Overview of recent global economic shifts
- The impact of tariffs and trade agreements on global commerce
- Key drivers of change: geopolitical tensions, regional economic blocs, and trade barriers
2. Economic Evolution by Continent
A - North America
- United States: Trade policies, impact of USMCA (United States-Mexico-Canada Agreement), and relations with China and Europe
- Trade Volume (2023): $4.9 trillion in exports, $3.3 trillion in imports
- Major Sectors Affected: Technology, automotive, agriculture
- Trend: Increasing focus on domestic manufacturing and reshoring of key industries (e.g., semiconductors)
- Canada: Balancing USMCA benefits with EU (CETA) and Asia-Pacific partnerships
- Trade Volume (2023): $680 billion in exports, $650 billion in imports
- Key Trading Partners: US (75% of exports), EU, China
- Trend: Rising investments in green technology and energy exports
- Mexico: Growth in nearshoring, strengthened trade with North America and Latin America
- Trade Volume (2023): $575 billion in exports, $550 billion in imports
- Key Industries: Automotive, electronics, textiles
- Trend: Near-shoring from Asia to Mexico for supply chain resilience
B - Europe
- EU Trade Strategy: European Green Deal, digital economy, and trade diversification
- Total EU Trade (2023): $6.8 trillion
- Major Sectors: Renewable energy, pharmaceuticals, financial services
- Trend: Expansion of digital trade and stricter environmental regulations impacting imports
- Brexit Impact: UK trade shifts post-Brexit, focus on CPTPP and bilateral agreements
- UK Trade Volume (2023): $1.2 trillion
- Main Partners: EU, US, Commonwealth nations
- Trend: Increasing trade with Asia-Pacific markets as a diversification strategy
C - Asia
- China: Belt and Road Initiative (BRI), trade war adjustments, and regional dominance
- Trade Volume (2023): $6.3 trillion in exports, $5.1 trillion in imports
- Key Sectors: Electronics, machinery, rare earth materials
- Trend: Shift toward self-sufficiency in critical industries due to US sanctions
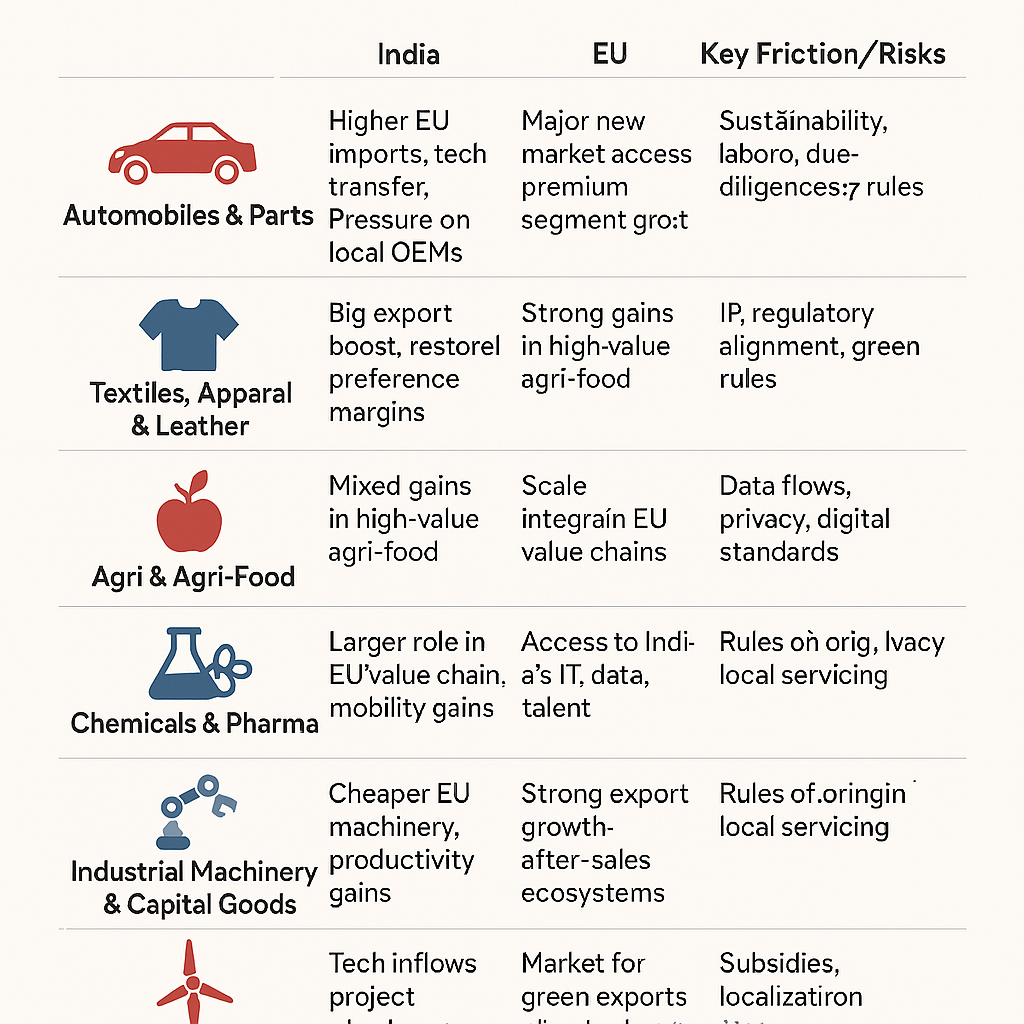
- India: Tariff adjustments, “Make in India” initiative, and emerging trade pacts
- Trade Volume (2023): $775 billion in exports, $900 billion in imports
- Key Growth Sectors: IT services, pharmaceuticals, textile manufacturing
- Trend: Surge in foreign direct investments (FDI) in manufacturing and technology
- ASEAN: RCEP (Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership) and intra-Asian trade expansion
- Trade Volume (2023): $3.5 trillion
- Key Contributors: Singapore, Indonesia, Vietnam, Thailand
- Trend: ASEAN becoming a major hub for global supply chain diversification
D - South America
- Brazil & Argentina: Economic restructuring, MERCOSUR challenges, and new partnerships
- Brazil Trade Volume (2023): $400 billion
- Argentina Trade Volume (2023): $150 billion
- Trend: Growth in agricultural exports, especially soybeans and meat products
- Chile & Peru: Growing ties with Asia and North America
- Key Sectors: Mining (copper, lithium), agriculture, fisheries
- Trend: Increasing investments in lithium extraction due to global EV demand
E - Africa
- AfCFTA (African Continental Free Trade Area): Impact on intra-African trade and global positioning
- Projected Growth: Intra-African trade to increase by 52% by 2030
- Trend: Rising infrastructure investments to facilitate trade
- Key Economic Hubs: Nigeria, South Africa, and Egypt as trade gateways
- Trade Volume (2023): Nigeria ($120 billion), South Africa ($300 billion), Egypt ($180 billion)
- Major Sectors: Energy, mining, digital economy
- Trend: Rapid expansion of mobile fintech and digital banking
F - Oceania
- Australia & New Zealand: Focus on Indo-Pacific trade, CPTPP participation, and China’s shifting economic influence
- Trade Volume (2023): Australia ($780 billion), New Zealand ($120 billion)
- Key Sectors: Agriculture, minerals, renewable energy
- Trend: Increased trade with India and Southeast Asia due to geopolitical tensions with China
3. Offshoring and Nearshoring Trends by Continent and Trade Agreement
- North America: Growth in nearshoring due to USMCA, benefiting Mexico with manufacturing investments
- Europe: Increased nearshoring within the EU, with Eastern Europe and Turkey emerging as key locations for manufacturing and IT services
- Asia: China losing some offshoring appeal due to tariffs, with Vietnam, India, and Indonesia attracting more manufacturing
- South America: Brazil and Mexico gaining prominence for nearshoring due to trade incentives with North America and the EU
- Africa: Emerging nearshoring hub, particularly in Morocco, Egypt, and South Africa, driven by AfCFTA
- Oceania: Australia increasing near-shoring within Southeast Asia, leveraging CPTPP for supply chain resilience
4. Conclusion & Strategic Recommendations
- Businesses: Adapting to logistics cost changes, diversifying shipping routes
- Governments: Investing in resilient logistics infrastructure and sustainable transport
- Investors: Opportunities in logistics technology, alternative energy-powered freight, and port expansions